MyBatis流程(第二阶段)
作者:IT王小二
代理封装阶段:封装 iBatis 的编程模型,使用 mapper 接口开发的初始化工作,那么这两行代码的背后到底是怎么为我们创建TUserMapper的实现类的呢?
// --------------------第二阶段---------------------------
// 2.获取sqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 3.获取对应mapper
TUserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(TUserMapper.class);我们还可以这样调用,但是我们平时开发过程中却从来没有手动调用,但是实际上,最后执行时还是使用这种方式来操作的,MyBatis帮我们封装了这个过程,让实际开发过程面向接口来调用。
// 2.获取sqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 3.执行查询语句并返回结果
TUser user = sqlSession.selectOne("com.enjoylearning.mybatis.mapper.TUserMapper.selectByPrimaryKey", 2);一、SqlSession
第二个阶段使用到的第一个对象就是 SqlSession,SqlSession 是 MyBaits 对外提供的最关键的核心接口,通过它可以执行数据库读写命令、获取映射器、管理事务等。
SqlSession 也意味着客户端与数据库的一次连接,客户端对数据库的访问请求都是由SqlSession来处理的,SqlSession 由 SqlSessionFactory 创建,每个 SqlSession 都会引用 SqlSessionFactory 中全局唯一单例存在的 configuration 对象,如下图所示:
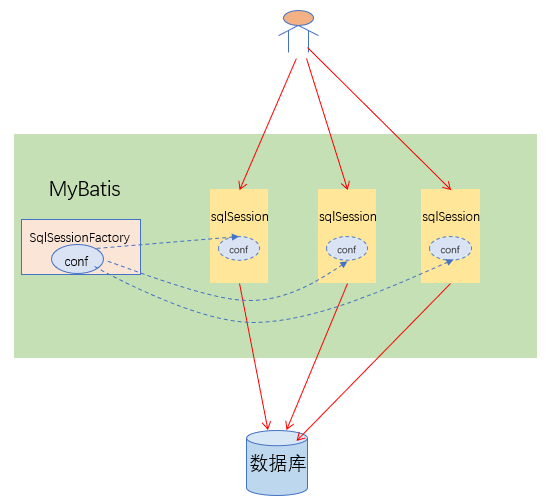
SqlSession 默认实现类为 org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession,解读如下:
- SqlSession 是 MyBatis 的门面,是 MyBatis 对外提供数据访问的主要 API,实例代码: com.enjoylearning.mybatis.MybatisDemo.originalOperation() 。
- 实际上 Sqlsession 的功能都是基于 Executor 来实现的,遵循了单一职责原则,例如:在 SqlSession 中的各种查询形式,最终会把请求转发到 Executor.query 方法。
二、SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory 使用工厂模式创建 SqlSession ,其默认的实现类为 DefaultSqlSessionFactory,其中获取 SqlSession 的核心方法为 openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType, TransactionIsolationLevel, boolean),在这个方法中从 configuration 中获取的 TransactionFactory 是典型的 策略模式 的应用。
运行期,TransactionFactory 接口的实现,是由配置文件配置决定的,可配置选项包括:JDBC、Managed,可根据需求灵活的替换 TransactionFactory 的实现,配置文件如下:
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc_driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc_url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc_username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc_password}" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>三、binding模块核心类
- MapperRegistry:mapper 接口和对应的代理对象工厂的注册中心。
- MapperProxyFactory:用于生成 mapper 接口动态代理的实例对象,保证 Mapper 实例对象是局部变量。
- MapperProxy:实现了 InvocationHandler 接口,它是增强 mapper 接口的实现。
- MapperMethod:封装了 Mapper 接口中对应方法的信息,以及对应的 sql 语句的信息。它是 mapper 接口与映射配置文件中 sql 语句的桥梁,MapperMethod 对象不记录任何状态信息,所以它可以在多个代理对象之间共享,MapperMethod 内几个关键数据结构。
- SqlCommand: 从 configuration 中获取方法的命名空间.方法名以及 SQL 语句的类型。
- MethodSignature:封装 mapper 接口方法的相关信息(入参,返回类型)。
- ParamNameResolver: 解析 mapper 接口方法中的入参,将多个参数转成 Map 。
四、整体流程分析
前面提到了 SqlSession 的默认实现类是 DefaultSqlSession,所以我们来看下这个 getMapper(Class<T> type) 方法到底干了些什么事情。
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}可以看到这里调用了 Configuration 类中的 getMapper(type, this) 方法,我们去看一下,这个在第一阶段中已经初始化过的信息(里面保存了mapper接口和对应代理对象工厂)。
/**
* mapper接口的动态代理注册中心
*/
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}看到里面继续从 mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession) 获取,继续往下看,进入了 MapperRegistry 类。
/**
* 用于生成mapper接口动态代理的实例对象
*/
public class MapperRegistry {
/**
* config对象,mybatis全局唯一的
*/
private final Configuration config;
/**
* 记录了mapper接口与对应MapperProxyFactory之间的关系
*/
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 通过class类型获取对应的代理工厂
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
// 通过一个代理工厂new出一个代理对象
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public <T> boolean hasMapper(Class<T> type) {
return knownMappers.containsKey(type);
}
/**
* 将mapper接口的工厂类添加到mapper注册中心,一阶段调用
*/
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// 实例化Mapper接口的代理工程类,并将信息添加至knownMappers
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
// 解析接口上的注解信息,并添加至configuration对象
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
// 省略其他代码
}可以看到通过class类型获取对应的代理工厂,然后通过一个代理工厂new出一个代理对象,继续往下看一下 newInstance 里面做了什么事情。
/**
* 用于生成mapper接口动态代理的实例对象
*/
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
/**
* mapper接口的class对象
*/
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
/**
* key是mapper接口中的某个方法的method对象
* value是对应的MapperMethod
* MapperMethod对象不记录任何状态信息,所以它可以在多个代理对象之间共享
*/
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
// 创建实现了mapper接口的动态代理对象
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 每次调用都会创建新的MapperProxy对象
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
// 省略其他代码
}可以看到这里就通过 代理模式动态的 创建出了我们想要的 接口实现类 了。
那么代理工厂只负责实例化接口对象,那么对对象方法实现的增强在哪里呢?我们去看一下 MapperProxy类。
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
/**
* 记录关联的sqlsession对象
*/
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
/**
* mapper接口对应的class对象
*/
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
/**
* key是mapper接口中的某个方法的method对象
* value是对应的MapperMethod
* MapperMethod对象不记录任何状态信息,所以它可以在多个代理对象之间共享
*/
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache;
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// 如果是Object本身的方法不增强
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
// 从缓存中获取mapperMethod对象,如果缓存中没有,则创建一个,并添加到缓存中,调用execute方法执行sql语句
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
/**
* 从缓存中获取mapperMethod对象,如果缓存中没有,则创建一个,并添加到缓存中
*/
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, m -> {
if (m.isDefault()) {
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}
interface MapperMethodInvoker {
Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable;
}
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
/**
* 封装了 Mapper 接口中对应方法的信息,以及对应的 sql 语句的信息
*/
private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;
public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {
super();
this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;
}
/**
* 调用execute方法执行sql
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
}至于 MapperMethod 对象,其中封装了 Mapper 接口中对应方法的信息,以及对应的 sql 语句的信息,其中包含了两个内部静态类,其中对应关系为如下:
public class MapperMethod {
/**
* 从configuration中获取方法的命名空间.方法名以及SQL语句的类型
*/
private final SqlCommand command;
/**
* 封装mapper接口方法的相关信息(入参,返回类型)
*/
private final MethodSignature method;
public static class SqlCommand {
/**
* sql的名称,命名空间+方法名称
*/
private final String name;
/**
* 获取sql语句的类型,select,insert,update,delete
*/
private final SqlCommandType type;
// 省略其他代码
}
public static class MethodSignature {
/**
* 返回参数是否为集合类型或数组
*/
private final boolean returnsMany;
/**
* 返回参数是否为map
*/
private final boolean returnsMap;
/**
* 返回值为空
*/
private final boolean returnsVoid;
/**
* 返回值是否为游标类型
*/
private final boolean returnsCursor;
/**
* 返回值是否为Optional
*/
private final boolean returnsOptional;
/**
* 返回值类型
*/
private final Class<?> returnType;
private final String mapKey;
private final Integer resultHandlerIndex;
private final Integer rowBoundsIndex;
/**
* 该方法的参数解析器
*/
private final ParamNameResolver paramNameResolver;
// 省略其他代码
}
// 省略其他代码
}