MyBatis缓存模块分析
作者:IT王小二
在 MyBatis 中一级缓存默认开始,二级缓存默认不开启(实际使用中也不会使用,一般使用 Redis 代替了)。
为了保证 MyBatis 的核心功能具有各种附加能力(防止缓存击穿,添加缓存情况策略(fifo、LRU),序列化功能,日志能力和定时清空能力等),缓存模块使用了 装饰器模式。
一、缓存模块结构
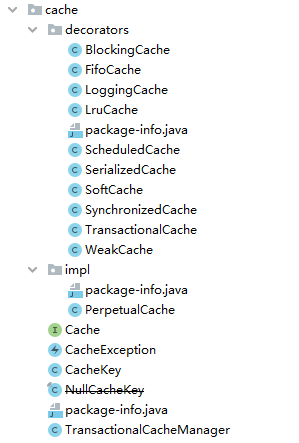
二、装饰器模式在缓存模块的使用
- Cache:Cache 接口是缓存模块的核心接口,定义了缓存的基本操作。
- PerpetualCache:在缓存模块中扮演 ConcreteComponent 角色,使用 HashMap 来实现 cache 的相关操作。
- BlockingCache:阻塞版本的缓存装饰器,保证只有一个线程到数据库去查找指定的 key 对应的数据。
- LoggingCache:日志能力的缓存装饰器。
- ScheduledCache:定时清空的缓存装饰器。
- SerializedCache:序列化能力的缓存装饰器。
- SynchronizedCache:进行同步控制的缓存装饰器。
三、核心功能类
1. Cache 接口
/**
* Cache 接口是缓存模块的核心接口,定义了缓存的基本操作
*/
public interface Cache {
/**
* 缓存实现类的id
*/
String getId();
/**
* 往缓存中添加数据,key一般是CacheKey对象
*/
void putObject(Object key, Object value);
/**
* 根据指定的key从缓存获取数据
*/
Object getObject(Object key);
/**
* 根据指定的key从缓存删除数据
*/
Object removeObject(Object key);
/**
* 清空缓存
*/
void clear();
/**
* 获取缓存的个数
*/
int getSize();
/**
* 取得读写锁, 从3.2.6开始没用了
*/
default ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() {
return null;
}
}2. PerpetualCache
/**
* Mybatis 为 Cache 接口提供的唯一一个核心实现类就是 PerpetualCache,其他类只是作为装饰器使用
*/
public class PerpetualCache implements Cache {
private final String id;
// 使用map来实现缓存
private final Map<Object, Object> cache = new HashMap<>();
public PerpetualCache(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return id;
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return cache.size();
}
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
return cache.get(key);
}
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
return cache.remove(key);
}
@Override
public void clear() {
cache.clear();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (getId() == null) {
throw new CacheException("Cache instances require an ID.");
}
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof Cache)) {
return false;
}
Cache otherCache = (Cache) o;
return getId().equals(otherCache.getId());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
if (getId() == null) {
throw new CacheException("Cache instances require an ID.");
}
return getId().hashCode();
}
}四、装饰器类
装饰器类太多,以其中一个来分析,毕竟读源码是读思想,而不是为了记住每一行代码什么意思,以BlockingCache为例。
/**
* 阻塞版本的缓存装饰器,保证只有一个线程到数据库去查找指定的key对应的数据
*/
public class BlockingCache implements Cache {
/**
* 阻塞的超时时长
*/
private long timeout;
/**
* 被装饰的底层对象,一般是PerpetualCache
*/
private final Cache delegate;
/**
* 锁对象集,粒度到key值(CacheKey后面分析)
*/
private final ConcurrentHashMap<Object, ReentrantLock> locks;
public BlockingCache(Cache delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
this.locks = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return delegate.getId();
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return delegate.getSize();
}
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
try {
delegate.putObject(key, value);
} finally {
releaseLock(key);
}
}
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
// 根据key获得锁对象,获取锁成功加锁,获取锁失败阻塞一段时间重试
acquireLock(key);
Object value = delegate.getObject(key);
if (value != null) {
// 获取数据成功的,要释放锁
releaseLock(key);
}
return value;
}
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
// despite of its name, this method is called only to release locks
releaseLock(key);
return null;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
delegate.clear();
}
private ReentrantLock getLockForKey(Object key) {
// 创建锁,把新锁添加到locks集合中,如果添加成功使用新锁,如果添加失败则使用locks集合中的锁,和下面代码效果相同
// ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// ReentrantLock previous = locks.putIfAbsent(key, lock);
// return previous == null ? lock : previous;
return locks.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ReentrantLock());
}
/**
* 根据key获得锁对象,获取锁成功加锁,获取锁失败阻塞一段时间重试
*/
private void acquireLock(Object key) {
// 获得锁对象
Lock lock = getLockForKey(key);
if (timeout > 0) {
try {
// 尝试拿锁,如果 timeout 没有拿到锁则抛出异常
boolean acquired = lock.tryLock(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (!acquired) {
throw new CacheException("Couldn't get a lock in " + timeout + " for the key " + key + " at the cache " + delegate.getId());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new CacheException("Got interrupted while trying to acquire lock for key " + key, e);
}
} else {
// 直接加锁
lock.lock();
}
}
private void releaseLock(Object key) {
ReentrantLock lock = locks.get(key);
if (lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public long getTimeout() {
return timeout;
}
public void setTimeout(long timeout) {
this.timeout = timeout;
}
}五、缓存的唯一标识 CacheKey
MyBatis 中涉及到动态 SQL 的原因,缓存项的 key 不能仅仅通过一个 String 来表示,所以通过 CacheKey 来封装缓存的 Key 值,CacheKey 可以封装多个影响缓存项的因素;判断两个 CacheKey 是否相同关键是比较两个对象的hash值是否一致;构成CacheKey对象的要素包括:
- mappedStatment 的 id
- 指定查询结果集的范围(MyBatis自带分页信息,我们一般不会使用自带的分页,所以重要的是其他的三个)
- 查询所使用的 SQL 语句
- 用户传递给 SQL 语句的实际参数值
转换到 CacheKey 代码如下,其中两个方法比较重要。
public class CacheKey implements Cloneable, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1146682552656046210L;
public static final CacheKey NULL_CACHE_KEY = new CacheKey() {
@Override
public void update(Object object) {
throw new CacheException("Not allowed to update a null cache key instance.");
}
@Override
public void updateAll(Object[] objects) {
throw new CacheException("Not allowed to update a null cache key instance.");
}
};
private static final int DEFAULT_MULTIPLIER = 37;
private static final int DEFAULT_HASHCODE = 17;
/**
* 参与hash计算的乘数
*/
private final int multiplier;
/**
* CacheKey的hash值,在update函数中实时运算出来的
*/
private int hashcode;
/**
* 校验和,hash值的和
*/
private long checksum;
/**
* updateList的中元素个数
*/
private int count;
// 8/21/2017 - Sonarlint flags this as needing to be marked transient. While true if content is not serializable, this
// is not always true and thus should not be marked transient.
/**
* 由该集合中的所有对象来共同决定两个 CacheKey 是否相等
*/
private List<Object> updateList;
public CacheKey() {
this.hashcode = DEFAULT_HASHCODE;
this.multiplier = DEFAULT_MULTIPLIER;
this.count = 0;
this.updateList = new ArrayList<>();
}
public CacheKey(Object[] objects) {
this();
updateAll(objects);
}
public int getUpdateCount() {
return updateList.size();
}
public void update(Object object) {
// 获取object的hash值
int baseHashCode = object == null ? 1 : ArrayUtil.hashCode(object);
// 更新count、checksum以及hashcode的值
count++;
checksum += baseHashCode;
baseHashCode *= count;
hashcode = multiplier * hashcode + baseHashCode;
// 将对象添加到updateList中
updateList.add(object);
}
public void updateAll(Object[] objects) {
for (Object o : objects) {
update(o);
}
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object object) {
// 比较是不是同一个对象
if (this == object) {
return true;
}
// 是否类型相同
if (!(object instanceof CacheKey)) {
return false;
}
final CacheKey cacheKey = (CacheKey) object;
// hashcode是否相同
if (hashcode != cacheKey.hashcode) {
return false;
}
// checksum是否相同
if (checksum != cacheKey.checksum) {
return false;
}
// count是否相同
if (count != cacheKey.count) {
return false;
}
// 如果前几项都不满足,则循环遍历 updateList 集合,比较元素的hashcode,判断每一项是否相等,如果有一项不相等则这两个CacheKey不相等
for (int i = 0; i < updateList.size(); i++) {
Object thisObject = updateList.get(i);
Object thatObject = cacheKey.updateList.get(i);
if (!ArrayUtil.equals(thisObject, thatObject)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return hashcode;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringJoiner returnValue = new StringJoiner(":");
returnValue.add(String.valueOf(hashcode));
returnValue.add(String.valueOf(checksum));
updateList.stream().map(ArrayUtil::toString).forEach(returnValue::add);
return returnValue.toString();
}
@Override
public CacheKey clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
CacheKey clonedCacheKey = (CacheKey) super.clone();
clonedCacheKey.updateList = new ArrayList<>(updateList);
return clonedCacheKey;
}
}六、缓存功能的入口在哪呢
- 二级缓存入口:
org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor.query(MappedStatement, Object, RowBounds, ResultHandler) - 一级缓存入口:
org.apache.ibatis.executor.BaseExecutor.query(MappedStatement, Object, RowBounds, ResultHandler)
接下来来分析一个这个流程
1、二级缓存方法,所属类:org.apache.ibatis.executor.CachingExecutor
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 获取sql语句信息,包括占位符,参数等信息
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 拼装缓存的key值
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
// 查询二级缓存
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
/**
* 查询二级缓存
*/
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
// 从MappedStatement中获取二级缓存
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
// 如果二级缓存不为null
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
// 从二级缓存中获取数据
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
// 二级缓存为空,才会调用BaseExecutor.query查询一级缓存
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
// 如果二级缓存为null则直接查询一级缓存
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}2、一级缓存方法,所属类:org.apache.ibatis.executor.BaseExecutor
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 获取sql语句信息,包括占位符,参数等信息
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 拼装缓存的key值
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
// 查询一级缓存
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
/**
* 查询一级缓存
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
// 检查当前executor是否关闭
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 非嵌套查询,并且FlushCache配置为true,则需要清空一级缓存,判断比如maper.xml里面select方法设置了flushCache="true"属性
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
// 查询层次加一
queryStack++;
// 查询一级缓存
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
// 针对调用存储过程的结果处理
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 缓存未命中,从数据库加载数据
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
// 延迟加载处理
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
// 如果当前sql的一级缓存配置为STATEMENT,查询完即清空一级缓存
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}总结一下:
- 先去查找二级缓存,如果二级缓存未找到数据,则去查询一级缓存。
- 一级缓存未找到数据则查询数据库。
七、Mybatis 的缓存功能使用 HashMap 实现会不会出现并发安全的问题?
答案当然是不会啦,原因如下:
- 二级缓存是多个会话共享的缓存,确实会出现并发安全的问题,因此 MyBatis 在初始化二级缓存时,会给二级缓存默认加上 SynchronizedCache 装饰器的增强,在对共享数据 HashMap 操作时进行同步控制,所以二级缓存不会出现并发安全问题。
- 一级缓存是会话独享的,不会出现多个线程同时操作缓存数据的场景,因此一级缓存也不会出现并发安全的问题。